Generative AI
How to Choose the Right Generative AI Model for Your Business
Generative AI is an artificial intelligence system designed to create new content, such as images, videos, music, or 3D models, without direct human involvement or instructions. These systems utilize advanced machine learning techniques to produce data that mimics the style and structure of the datasets on which they were trained.
Meanwhile, Generative AI models are designed to create new data that closely resembles the patterns and structures of the data they were trained on, to revolutionize content creation, enabling the automatic generation of high-quality and diverse outputs across various domains, from art and entertainment to science and engineering.
In this article, we will explore different types of Generative AI models that businesses can adopt to meet their emerging business requirements.
What Are Generative AI Models?
Generative AI models are a specialized class of machine learning systems designed to create new data that closely resembles the patterns and structures of the data they were trained on.
Unlike traditional AI models that focus on tasks like prediction or classification, generative models excel in producing original content, including images, text, music, videos, and even 3D models.
These models leverage advanced algorithms to understand the complexities of input data and use that understanding to generate new outputs that are both unique and realistic.
Types of Generative AI models
There are several types of generative AI models, each with its unique approach to generating content.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) – use a unique adversarial training process to create realistic data. They consist of two neural networks including a generator and a discriminator that work in competition with each other to improve the quality of the generated data.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) – learn to encode input data into a compressed latent representation and decode it back to reconstruct the original input. Unlike traditional autoencoders, VAEs are probabilistic, meaning they generate data by sampling from a learned distribution, enabling the creation of new, unique outputs.
- Transformer-based models – originally developed for natural language processing tasks, have emerged as a powerful tool for video anomaly detection due to their ability to model long-range dependencies and capture complex spatiotemporal patterns
- Diffusion models – have gained significant attention for their potential in video anomaly detection. These models learn to reverse a noise process that gradually corrupts data, effectively reconstructing the original data distribution. By leveraging this ability, diffusion models can model complex video datasets and identify anomalies as deviations from the learned normal distribution.
Examples of Generative AI models
Following are some famous examples of Generative AI models, being utilized by different business domains:
| Name of the model | Description | Type of the model |
| GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) | Designed for natural language understanding and generation. Applications include chatbots, content creation, and summarization. | Text-Based Model |
| BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) | A transformer-based language model for understanding, it serves as a foundation for many generative tasks when fine-tuned. | Text-Based Model |
| DALL·E | A transformer-based model by OpenAI that generates detailed images from textual descriptions. | Image-based model |
| WaveNet | Developed by DeepMind, it generates realistic human-like speech and high-quality audio. | Audio and speech models |
| VID2VID | Designed for video-to-video translation, such as converting sketches into realistic videos. | Video-based model |
| CLIP-Guided Diffusion | Combines vision and language models for generating images based on text descriptions. | Multimodal model |
How to choose the right Generative AI model for your business
Choosing the right generative AI model for your business involves understanding your specific needs, resources, and the type of content or functionality you aim to generate.
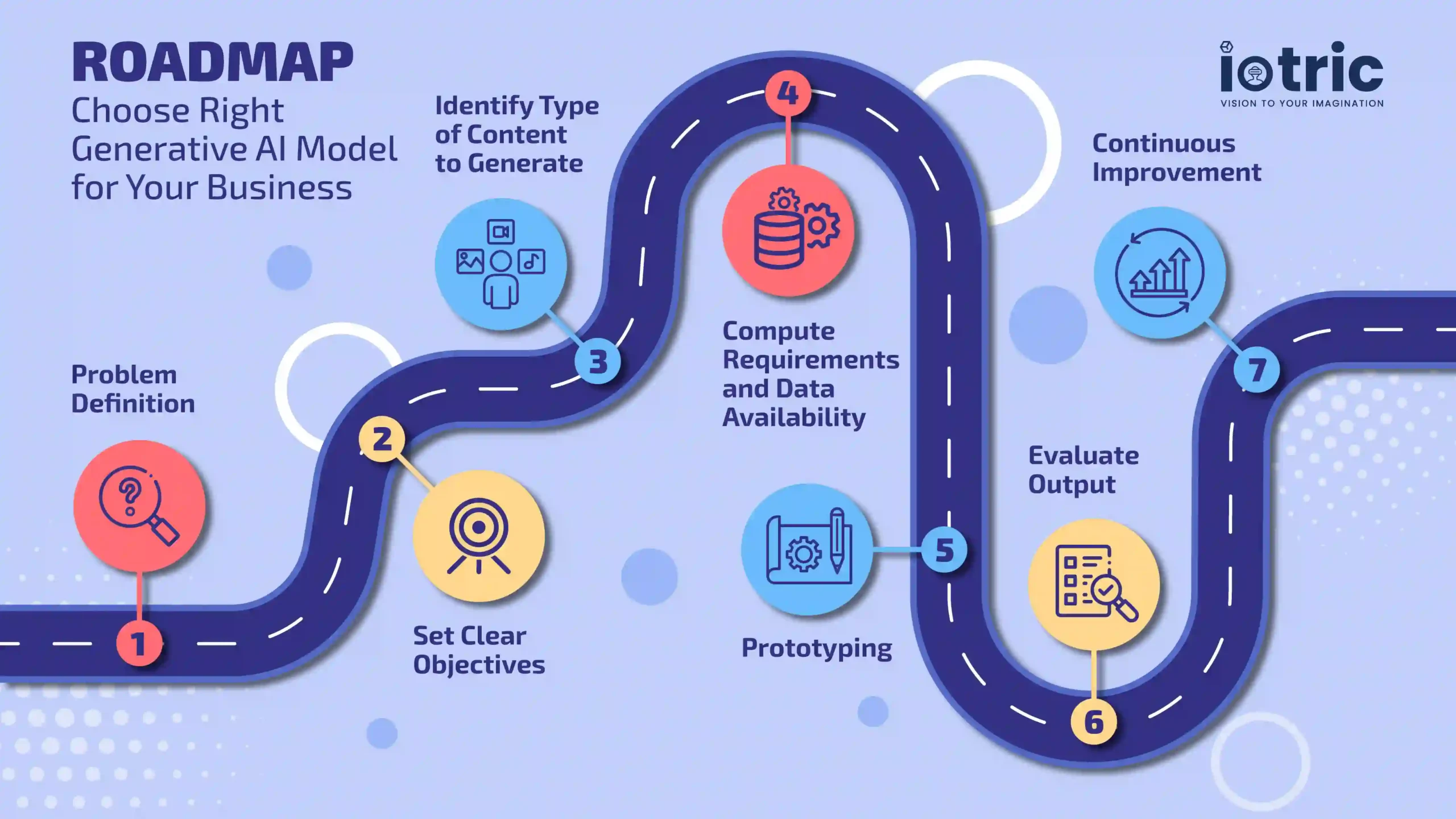
Following is a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Problem definition: Identify the specific challenge or opportunity you want to address.
2. Set clear objectives: Determine SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-based) goals.
3. Identify the type of content to generate: Different generative AI models specialize in various types of outputs. Choose a model based on the content your business needs:
| Type of Content | Use Cases | Examples |
| Text | For chatbots, content writing, summarization, or translation | GPT models |
| Images | For marketing, product design, or advertisements | DALL·E, Stable Diffusion, etc. |
| Audio | For creating music, voiceovers, or sound effects | WaveNet, Jukebox, etc. |
| Videos | For video generation, animation, or editing Runway | Gen-2, VID2VID, etc. |
| 3D Models | For virtual reality, gaming, or architecture | NeRF |
4. Compute Requirements and Data Availability: Ensure you have the necessary computational resources and relevant data for training or deployment, especially for resource-intensive models like GANs or diffusion models.
5. Prototyping: Start with a small-scale implementation to test the model’s performance in your specific business context.
6. Evaluate Output: Assess whether the generated content meets your quality standards and business needs.
7. Continuous Improvement: Once deployed, continuously monitor the model’s performance and optimize it to adapt to changing business needs or user feedback
Conclusion
Selecting the right generative AI model for your business is a strategic process that requires aligning your objectives with the model’s capabilities. By clearly defining your goals, understanding the type of content you need, and evaluating data availability, you can narrow down the options. It’s equally important to consider factors such as resource requirements, creativity, personalized experiences, and cost efficiency.